Table of content
- Impact of 2024 Hospital Network Cyberattack
- Understanding the Compliance Crisis in Healthcare
- The High Stakes of Compliance Gaps
- How to Identify and Close Risk Gaps
- The Role of Technology in Ensuring Compliance
- Partnering for Compliance Success
- Proactive Compliance: A Long-Term Strategy
- Conclusion
A Compliance Catastrophe Unfolded
In early 2024, a major U.S. hospital network suffered a crippling cyberattack. The breach compromised over 1.2 million patient records, halted operations across multiple states, and resulted in a $4.5 million HIPAA violation fine. More damaging than the financial penalty was the loss of patient trust – a toll far harder to restore.
This incident is not an outlier, but a warning signal to all healthcare institutions: compliance is no longer optional – it is mission critical.
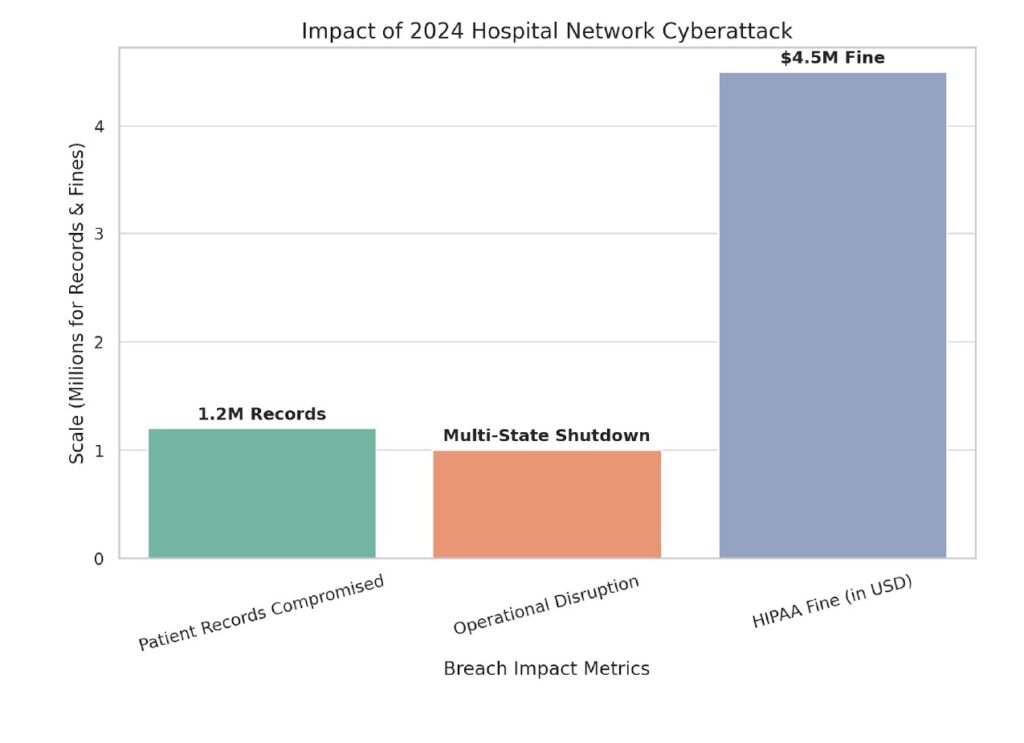
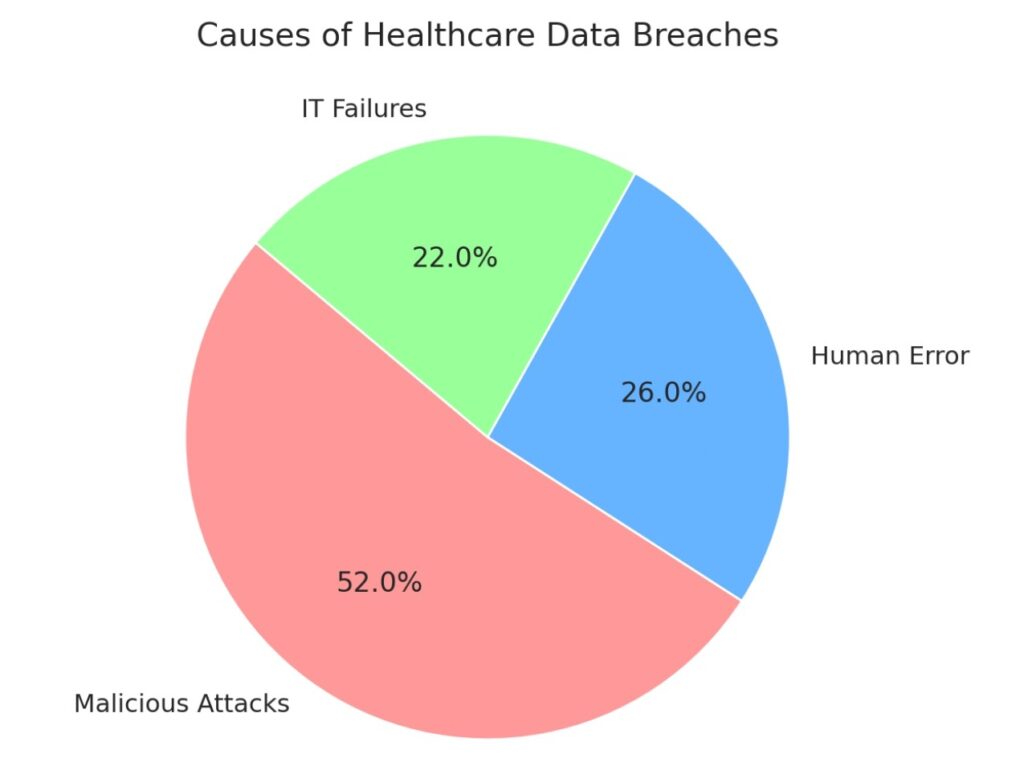
Here is the graphical representation of the 2024 hospital network cyberattack:
📉 Impact of 2024 Hospital Network Cyberattack
This chart illustrates:
- 1.2 million patient records compromised
- Multi-state operational disruption
- $4.5 million HIPAA violation fine
As cyber threats escalate and regulations grow increasingly stringent, the healthcare sector faces an unprecedented compliance crisis. With sensitive patient data stored across cloud systems, accessed remotely, and shared with third parties, organizations must adopt a security-first, compliance-aligned approach—or risk devastating consequences.
Understanding the Compliance Crisis in Healthcare
The regulatory environment in healthcare is complex and unforgiving. Core regulations include:
- HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) – mandates the secure handling of Protected Health Information (PHI).
- HITECH Act – reinforces HIPAA with stricter breach notification rules and higher penalties.
- GDPR (for global entities) – demands stringent consent, data handling, and cross-border data processing protocols.
Despite clear mandates, healthcare providers consistently fall short in critical areas:
1. Inadequate Data Handling & Storage
Unencrypted records, shared folders, and unmanaged mobile devices are still common, exposing patient data to unnecessary risk.
2. Weak Access Controls
Excessive privileges, shared credentials, and insufficient authentication mechanisms plague even top-tier health systems.
3. Third-Party/Vendor Risk
Business associates—from billing platforms to cloud service providers—often lack the same compliance rigor, multiplying the risk.
4. Lack of Employee Training
Most breaches stem from human error—phishing emails, misdirected communications, and failure to recognize suspicious activity.
5. Emerging Challenges with Modern Healthcare Delivery
The rapid expansion of telehealth, remote care, and cloud adoption introduces new vulnerabilities that traditional controls can’t manage alone.
The High Stakes of Compliance Gaps
Compliance is not just a checkbox. The implications of overlooking it are severe:
Financial Penalties
HIPAA violations can lead to civil fines up to $1.5 million per year, per violation type—and even higher for willful neglect. Legal fees and breach notification costs pile on.
Reputation Erosion
Healthcare runs on trust. A single incident can destroy a reputation built over decades, driving patients away.
Operational Disruption
Breaches trigger widespread IT shutdowns, disrupt appointments and surgeries, and cripple continuity of care.
Regulatory Scrutiny
Following a breach, regulators may impose Corrective Action Plans (CAPs), periodic audits, and detailed reporting obligations for years.
How to Identify and Close Risk Gaps
1. Conduct a Thorough Risk Assessment
Comprehensive audits are the cornerstone of compliance.
- Internal Assessments: Identify gaps in data handling, system configurations, and access controls.
- Third-Party Audits: Objective evaluations reveal blind spots often overlooked internally.
2. Enforce Strong Access Control Measures
Prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data through:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Only authorized personnel access the data they need.
- Identity & Access Management (IAM): Use federated identity, SSO, and MFA to secure every user and session.
3. Upgrade Legacy Systems
Outdated platforms can’t meet today’s compliance standards.
- Patch & Update Regularly: Eliminate known vulnerabilities.
- Migrate to Compliant Cloud Platforms: Ensure data sovereignty, encryption at rest and in transit, and compliance certifications.
4. Educate & Train Continuously
Human error remains the biggest security vulnerability.
- Compliance Training: Annual programs aligned to HIPAA and organizational policies.
- Phishing Simulations: Reinforce recognition of common attack methods.
- Security Awareness Campaigns: Foster a culture of security mindfulness.
5. Monitor & Respond in Real-Time
Proactive monitoring prevents small issues from becoming massive breaches.
- Compliance Monitoring Tools: Leverage continuous compliance platforms for real-time alerts.
Incident Response Plan: Define roles, actions, and communications for every security event.
The Role of Technology in Ensuring Compliance
Automated Compliance Management
Automation reduces human error and maintains audit-readiness year-round. Platforms track policy violations, audit trails, and real-time compliance gaps.
Advanced Cybersecurity Controls
Compliance is meaningless without security:
- Data Encryption: Secure data at rest and in transit using AES-256 or higher.
- Endpoint Protection: Secure workstations, mobile devices, and medical equipment.
- Secure Cloud Storage: Use HIPAA-compliant cloud services with robust redundancy and tamper-evident logs.
Centralized Compliance Dashboards
Consolidate compliance metrics, system statuses, audit logs, and training completion rates into a single view. These dashboards provide executive visibility and faster decision-making.
Partnering for Compliance Success
Why Bring in Experts?
Even with robust internal teams, partnering with cybersecurity consultants or managed service providers enhances resilience. These partners:
- Stay current with evolving regulations
- Provide specialized risk assessments
- Implement customized security frameworks
- Offer 24/7 incident response and monitoring
Selecting the Right Partner
Choose a partner with:
- Proven healthcare compliance experience
- Familiarity with HIPAA, HITECH, GDPR
- Capabilities in IAM, SIEM, endpoint protection, and threat intelligence
Proactive Compliance: A Long-Term Strategy
Compliance must shift from a reactive obligation to an embedded operational discipline.
- Build a Compliance-First Culture: Ingrain security and compliance into every department and function.
- Set Accountability: Designate responsible compliance officers and cross-functional champions.
- Integrate Tools and People: Combine policy, process, and platforms for holistic defense.
Ongoing gap analysis, regular training, and a culture of transparency foster organizational resilience and trust.
Conclusion
Healthcare organizations can no longer afford a reactive approach to compliance. The risks—financial, reputational, and operational—are simply too high. The compliance crisis is real, but so is the opportunity to transform.
We urge every healthcare leader to:
- Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment
- Upgrade outdated systems and practices
- Invest in technology that delivers real-time compliance insights
- Create a culture where every employee is a compliance advocate
Now is the time to act. Protect your patients, your data, and your institution’s future.
SOURCES